Glaucoma symptoms, treatment: Glaucoma silently steals vision from millions of people worldwide. This progressive eye disease damages the optic nerve slowly, often without warning signs, until severe vision loss occurs. Knowing about this condition arms you with knowledge to protect your eyesight and get timely treatment.
Why is glaucoma a hidden danger?
Most people with glaucoma don’t realise they have it. The disease typically begins by affecting peripheral vision, the edges of what you see, while leaving central vision intact. Your brain compensates for these blind spots so effectively that you might not notice vision changes until the disease reaches advanced stages. By then, permanent damage has already occurred.
Also Read | Do blue light glasses work? Here’s what the science says
Elevated eye pressure usually drives glaucoma development, though some people develop the condition despite normal pressure readings. The eye continuously produces a clear fluid called aqueous humour, which normally drains through tiny channels. When these drainage systems become blocked or inefficient, pressure builds inside the eye, gradually damaging delicate optic nerve fibres.
Who’s more at risk of glaucoma?
Age significantly increases glaucoma risk, with people over 60 facing higher chances of developing the disease. African Americans, Hispanics, and Asians experience elevated risk compared to other ethnic groups. Family history plays a crucial role; having relatives with glaucoma multiplies your likelihood of developing it.
Medical conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, and heart disease correlate with increased glaucoma risk. People who have experienced eye injuries, undergone certain eye surgeries, or taken corticosteroid medications for extended periods also face higher chances of developing this condition.
Signs of glaucoma:
Early-stage glaucoma rarely produces symptoms, making regular eye exams essential. However, acute angle-closure glaucoma announces itself dramatically with severe eye pain, headaches, nausea, vomiting, and sudden vision changes, including seeing halos around lights.
Chronic glaucoma progresses more subtly. You might notice gradually worsening peripheral vision, difficulty adjusting to darkness, or problems with glare sensitivity. Some people experience frequent changes in eyeglass prescriptions or mild eye discomfort.

How to detect glaucoma?
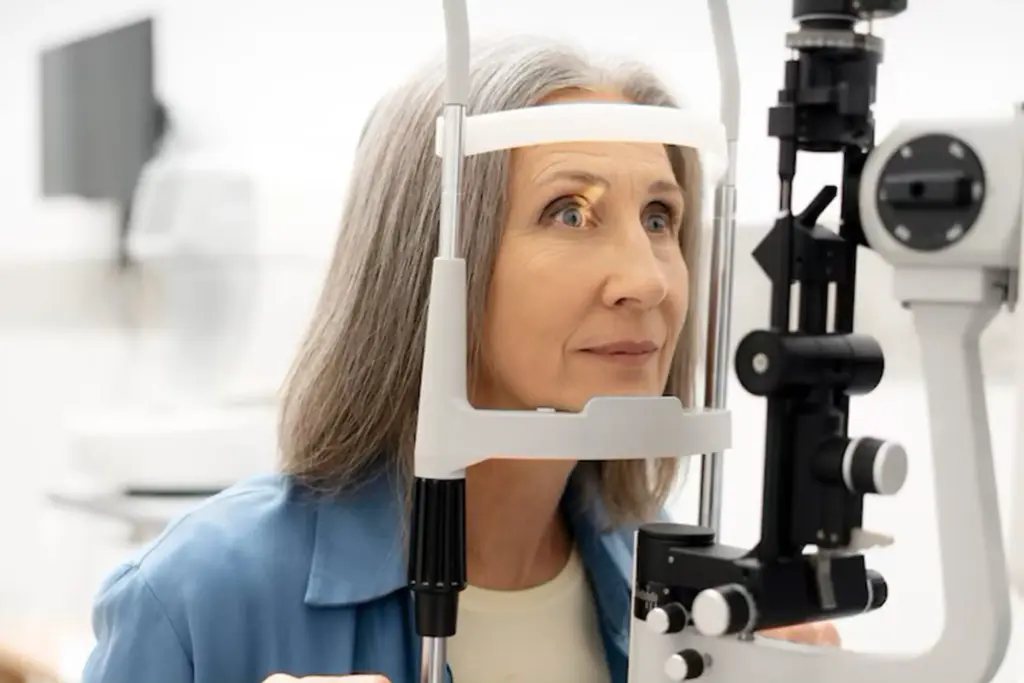
Comprehensive eye exams detect glaucoma before symptoms appear. Eye care professionals measure eye pressure, examine the optic nerve, and assess visual fields during these evaluations. Advanced imaging technologies now allow doctors to detect optic nerve changes years before traditional methods would catch them.
The American Academy of Ophthalmology recommends comprehensive eye exams every one to two years for people over 40, with more frequent screening for high-risk individuals. Don’t wait for symptoms; schedule your exam today.
How to treat glaucoma?
While doctors cannot reverse glaucoma damage, they can slow or halt disease progression through various treatments. Prescription eye drops reduce eye pressure by decreasing fluid production or improving drainage. Laser procedures create new drainage pathways or reduce fluid production. Surgical interventions become necessary when other treatments fail to control pressure adequately.
Success depends on early diagnosis and consistent treatment adherence. Patients who follow their treatment plans religiously often maintain functional vision throughout their lives.
Also Read | LASIK vs. SMILE vs. lenses: Which vision correction procedure is right for you?
Glaucoma’s silent nature makes prevention through regular screening your best defence. Schedule comprehensive eye exams, maintain healthy lifestyle habits, protect your eyes from injury, and discuss family history with your eye care provider. Early detection transforms this potentially blinding disease into a manageable condition, preserving your precious gift of sight for years to come.