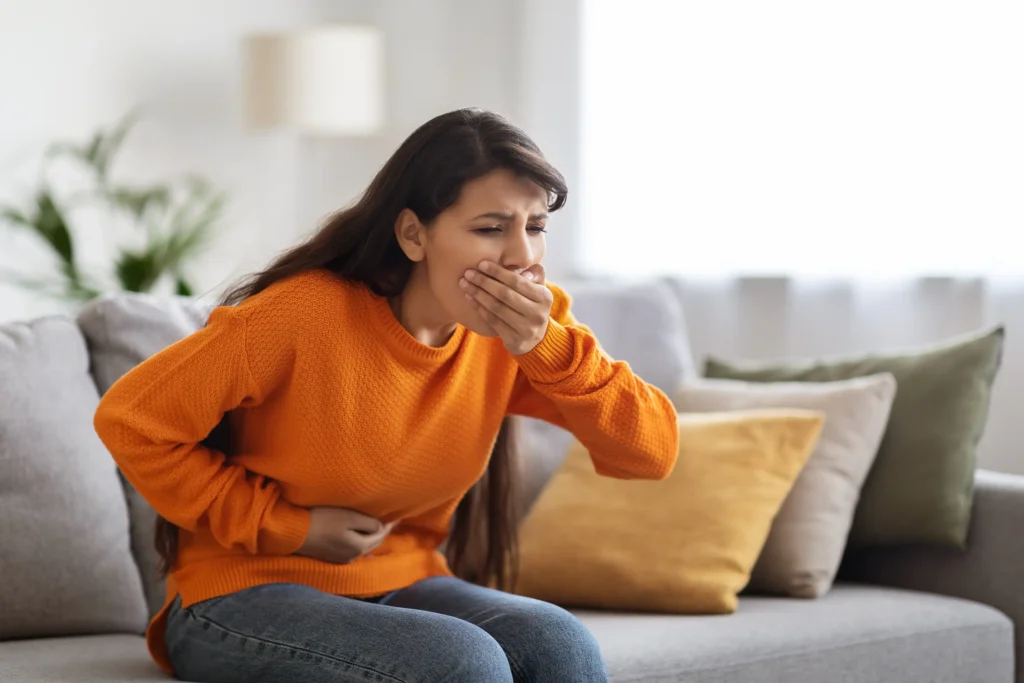
Gallbladder diseases: Your gallbladder may be small, but it plays an important role in digestion. This pear-shaped organ stores bile, a fluid that helps break down fats. When the gallbladder isn’t functioning properly, it can lead to painful conditions such as gallstones, infection, or inflammation.
Here are the factors that put you more at risk of developing gallbladder disease:
Gender and age:
Women are more likely than men to develop gallbladder disease, especially between the ages of 20 and 60. Hormones such as oestrogen raise cholesterol levels in bile, which can lead to gallstones.
Diet and obesity:
A diet high in fatty, fried, or processed foods increases the risk of gallstones. Being overweight or obese is another strong factor, as it raises cholesterol levels in the bile. Ironically, losing weight too quickly can also be risky. When you go on a very low-calorie diet or have bariatric surgery, your liver releases more cholesterol into your body.
Family history:
If gallbladder disease runs in your family, your risk is higher. Genetics can influence how your body processes cholesterol and bile, making you more prone to gallstone formation.
Also Read | How to dissolve gallstones without surgery: What works?
Pregnancy:
Pregnant women are at higher risk because hormonal changes can slow down gallbladder contractions and alter bile composition. Similarly, hormone replacement therapy or birth control pills can also influence gallstone formation.
Medical conditions:
Certain health conditions are linked to a greater risk of gallbladder disease. These include:
- Diabetes
- Metabolic syndrome
- Liver disease
- High cholesterol
- Blood disorders such as sickle cell anaemia
Symptoms of gallbladder disease:
Some common signs include sharp pain in the upper right of your belly, nausea or vomiting, and bloating or indigestion. If a gallstone blocks a bile duct, you might also get a fever.
Can gallbladder disease be prevented?
You can lower your risk by maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, and staying active.