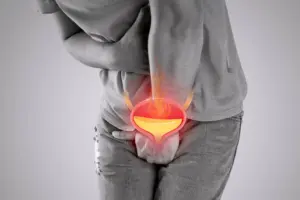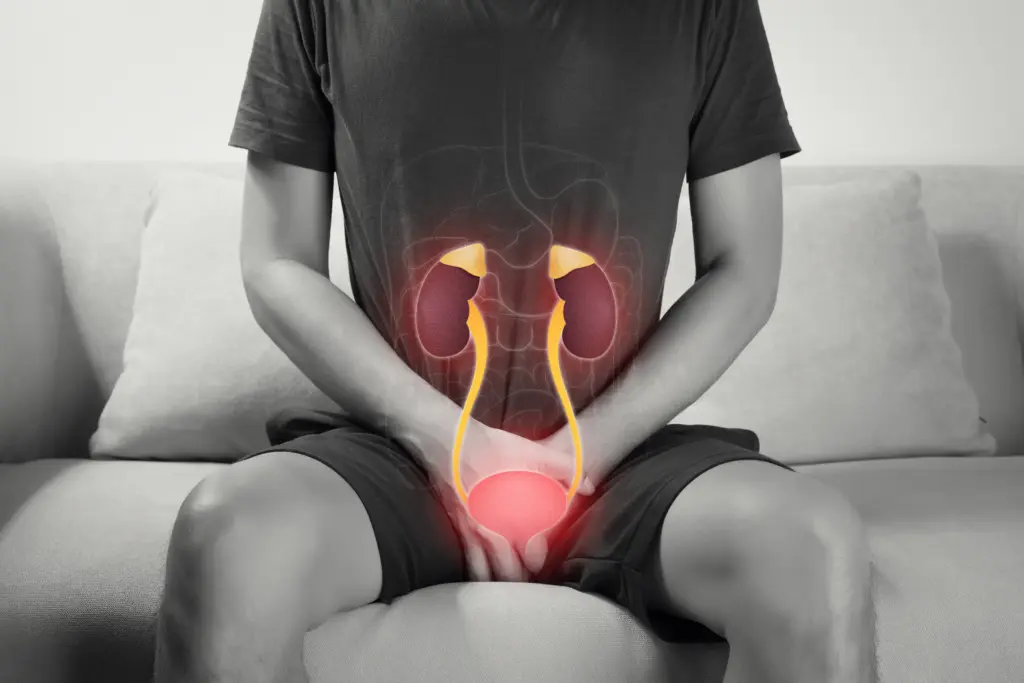
UTI symptoms & causes: Let’s be honest, urinary tract infections (UTIs) aren’t easy to talk about. But if you’ve had one, you know how uncomfortable and painful they can be. The good news: urinary tract infections are common, treatable, and often preventable once you understand the basics. This simple guide walks you through what a UTI is, why it happens, key symptoms to watch for, and the smartest ways to treat it and stop it from coming back.
What is a UTI?
A UTI (urinary tract infection) is an infection in any part of the urinary system: kidneys, bladder, or urethra. Most UTIs affect the lower tract (bladder and urethra). They’re very common and, when treated early, are usually straightforward and not serious.
Also Read | UTI vs. kidney infection: How to tell the difference
How do you get a UTI?
A UTI usually starts when bacteria enter the urinary tract. It is caused by E. coli, a germ that normally lives in the gut but can trigger infection if it reaches the urethra and bladder. It can get there more easily with habits like wiping back-to-front (women should wipe front-to-back), holding urine too long, or not drinking enough water. Sexual activity and poor genital hygiene can also introduce bacteria. Staying hydrated, emptying the bladder regularly, especially after sex, and front-to-back wiping help lower the risk.
Who gets UTI?
Anyone can get a urinary tract infection, but some people are more likely than others. Women face a higher risk because their urethra is shorter, allowing bacteria to reach the bladder more easily. Pregnant women are also more vulnerable since hormonal changes can affect how the urinary tract functions.
Older adults tend to experience UTIs more often, partly due to weaker immunity and age-related changes, while people with diabetes are more prone because high blood sugar creates a favourable environment for bacterial growth. Men with prostate issues can also be at greater risk, as an enlarged prostate may interfere with normal urine flow. Understanding these risk factors is key to prevention and timely treatment.

Common symptoms of UTI:
UTI symptoms vary with the infection’s location, but common signs include a burning sensation while urinating, a strong and frequent urge to pee with little output, and lower belly pain or pressure; some people also feel unusually tired or shaky. If the infection reaches the kidneys, symptoms can escalate to fever, chills, pain in the back or side, and nausea or vomiting. Kidney infections require prompt medical care.
How is UTI diagnosed?
If you think you have a UTI, see a doctor. They’ll review your symptoms and usually ask for a urine sample to check for bacteria; most cases are confirmed with this simple test. If infections keep coming back or seem severe, you may need further evaluation, such as a urine culture or an ultrasound, but that’s not typical for first-time, uncomplicated UTIs.
Also Read | Can sex cause UTIs? What you need to know and how to avoid them
UTIs are common, annoying, and sometimes painful, but highly treatable when caught early. Knowing the signs and acting fast matters. If you feel burning when you pee or a constant urge to go, don’t wait it out. Quick treatment eases discomfort and helps prevent more serious complications.